Team:NC School of Sci Math/Project
From 2013hs.igem.org
Revision as of 03:42, 3 June 2013 by Jack Allen (Talk | contribs)
2013
Home Team Project Details Lab Notebook Results Human Impact Biosafety Acknowledgments Official Team Profile
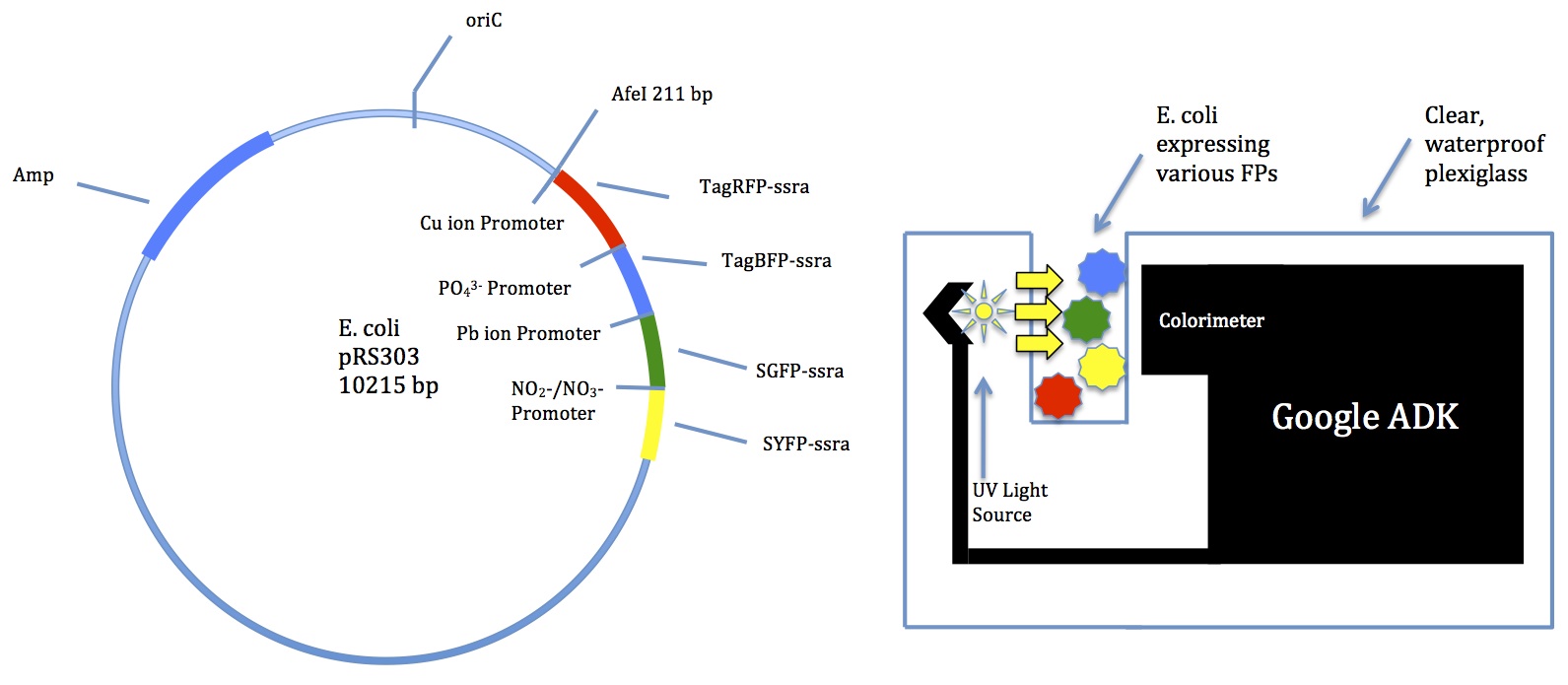
Project Proposal
Type Here
References
- Hooper LV, Midtvedt T, and Gordon JI. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu Rev Nutr 2002; 22 283-307.
- Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO, and Kasper DL. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell 2005 Jul 15; 122(1) 107-18.
- Donskey CJ. The role of the intestinal tract as a reservoir and source for transmission of nosocomial pathogens. Clin Infect Dis 2004 Jul 15; 39(2) 219-26.
- Suttie JW. The importance of menaquinones in human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 1995; 15 399-417.
- Krammer HJ, Kamper H, von Bunau R, Zieseniss E, Stange C, Schlieger F, Clever I, and Schulze J. Probiotic drug therapy with E. coli strain Nissle 1917 (EcN): results of a prospective study of the records of 3,807 patients. Z Gastroenterol 2006 Aug; 44(8) 651-6.
- Westendorf AM, Gunzer F, Deppenmeier S, Tapadar D, Hunger JK, Schmidt MA, Buer J, and Bruder D. Intestinal immunity of Escherichia coli NISSLE 1917: a safe carrier for therapeutic molecules. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2005 Mar 1; 43(3) 373-84.
- Rao S, Hu S, McHugh L, Lueders K, Henry K, Zhao Q, Fekete RA, Kar S, Adhya S, and Hamer DH. Toward a live microbial microbicide for HIV: commensal bacteria secreting an HIV fusion inhibitor peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005 Aug 23; 102(34) 11993-8.
- Duan F and March JC. Interrupting Vibrio cholerae infection of human epithelial cells with engineered commensal bacterial signaling. Biotechnol Bioeng 2008 Sep 1; 101(1) 128-34.
 "
"